|
SEO updates you need to know
Sponsor: Clearscope
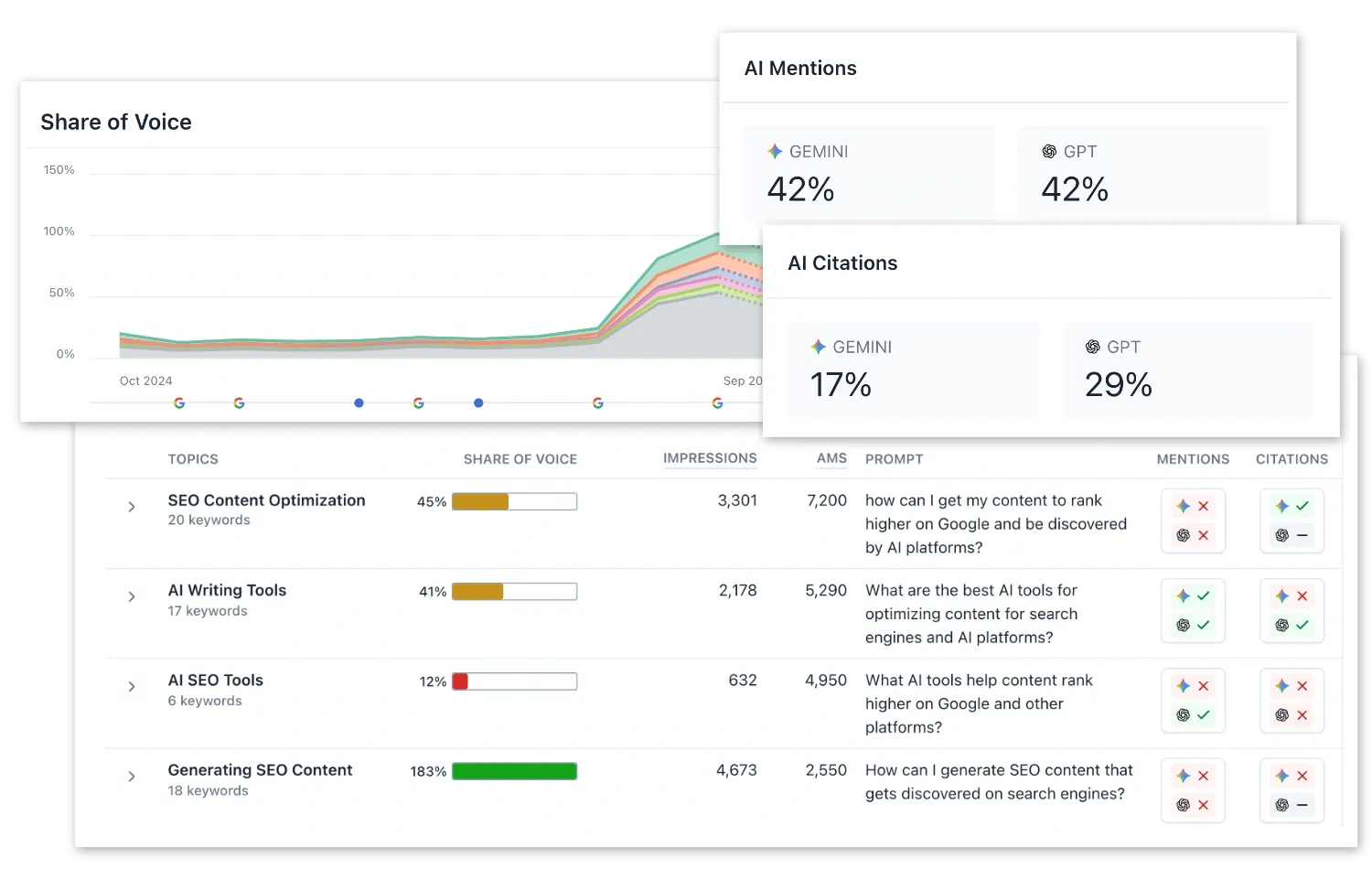
Get discovered on Gemini, ChatGPT, and what's next.
Clearscope helps you track prompts, monitor your brand's AI visibility, and optimize your content for maximum discoverability in an AI-first world.
Clearscope is trusted by 1,000s of customers including Webflow, Adobe, HubSpot, and Nvidia.
|
Search with Candour podcast

Video content is essential for your SEO in 2026
Season 4: Episode 54
Jack Chambers-Ward is joined by Georgie Kemp, the SEO lead at Veed.
Together, they delve into the limitless potential of video as a channel for marketers, discussing how video content can be repurposed and its SEO advantages.
Georgie emphasises the importance of authenticity and the human element in creating engaging video content. Jack and Georgie also explore the evolution of search, integrating video into SEO strategies, and leveraging AI while maintaining a human touch.
|
|
|
This week's solicited tips:
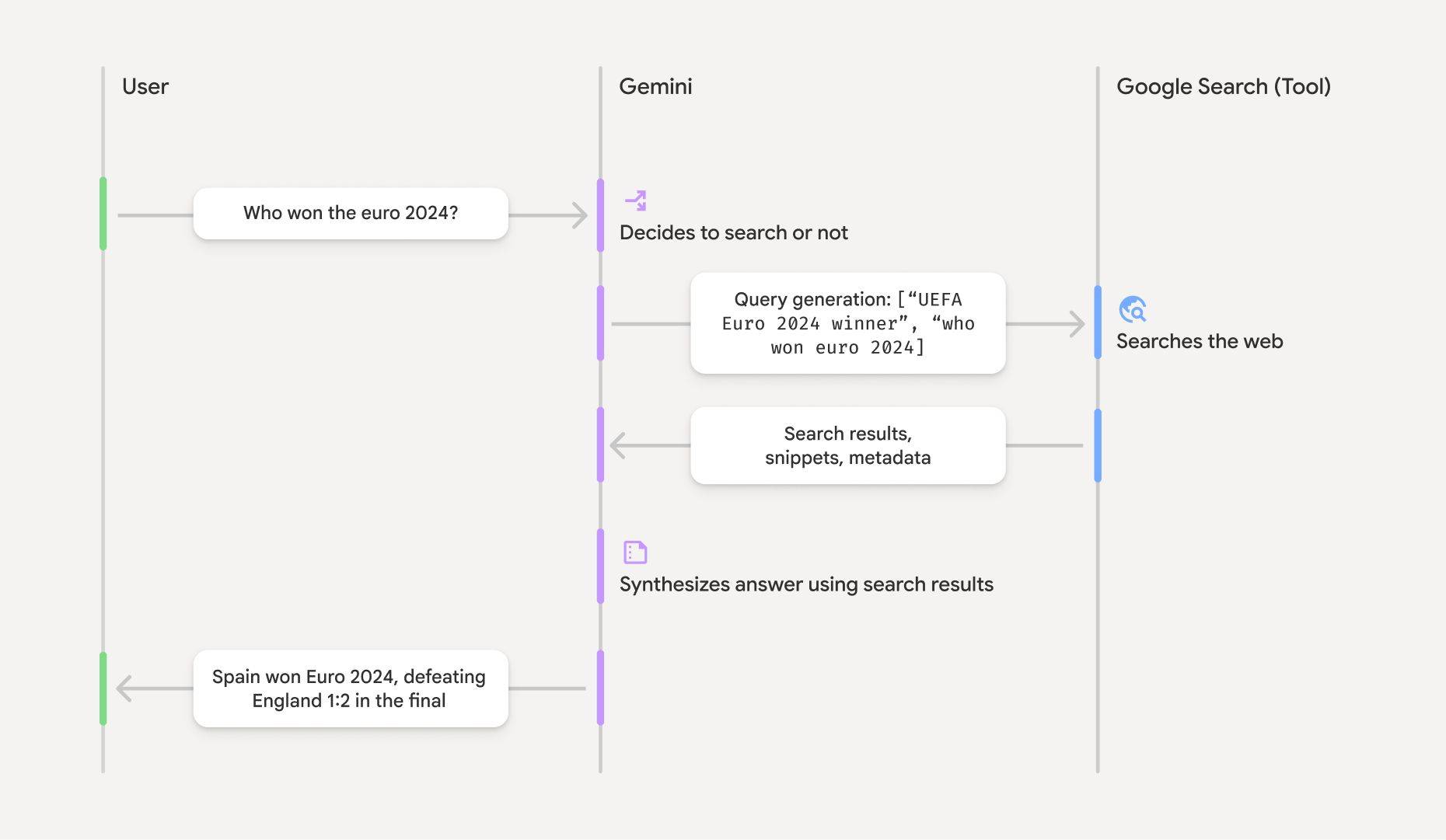
Your user has been, by thine own hand, revoked
One of the shifts with AI search is that more than ever, agents/bots are becoming the "user" in terms of interacting with search indexes.
So, how can we prepare for this? 🤔
One of the ways is understanding how and when AI systems are interacting with search. For instance, the Gemini model connects to Google Search which allows it to provide more accurate answers and cite verifiable sources beyond its knowledge cutoff.
There is actually a publicly available Gemini Grounding API. This allows you to easily see, at scale, which prompts are triggering grounding searches, and what searches those bots (users?) are performing. 💡
|

Apple's ambition should never exceed their worth
Android and Apple (iOS) together command approximately 99% of the global smartphone market together. Gemini is going to be running 99% of devices in peoples' hands. 📱
When doing interviews last year, I said that I felt Apple were one serious contender in the AI race against Google because they own a lot of the hardware in peoples' hands, and the hardware was key to being able to make AI agent assistants helpful through personalisation.
The ramifications of this collaboration is HUGE. Definitely going to spend more time understanding Gemini and making it core to strategies, rather than other models.
|
The content you've read, if nothing else, has been watered down
"Do you normally create one piece of content for each search variation? No matter how small the difference?" is a question I was asked twice last week after discussing intent research with AlsoAsked ⤵️
↔️ Query Breadth Determines Structure: Broad terms like "puppy training" generate diverse questions (e.g., best age to start, daily training minutes, basic commands). These warrant separate pages due to distinct intents. Narrow terms like "toilet train a dog" yield related sub-questions (e.g., time required, pee pads, stopping indoor accidents). These are best covered on one page.
❓ Prioritise Search Intent Over Exact Questions: Don't list or answer every question verbatim. Instead, cover the underlying user goal. For toilet training, include sections on duration, influencing variables (e.g., breed, age), products (e.g., pee pads), and challenges (e.g., smells that repel dogs).
Build Content Around User Goals: Related questions cluster around achieving a specific outcome (e.g., successful toilet training). Create sections addressing timelines, variables, products, and tips for puppies vs. older/rescue dogs to fully satisfy intent.
👋 It's a Human Task, Not AI: AI struggles with nuanced intent grouping. Humans excel by exploring question trees and focusing on user needs for superior content briefs.
📄 Allow Overlap Across Pages: Answer questions where they fit best. For example, overview articles can briefly touch on toilet training time, linking to in-depth pages with details like breed variations or speedup methods.
|

Images. Lots of images.
Images are often neglected when it comes to site migrations, but they can be big traffic drivers, especially for e-commerce websites. So what can we do? 🛒
Candour had an e-commerce client getting approximately 80,000 clicks from their product imagery, but they were replacing all of their images (and therefore image names/URLs) during a site rebuild and migration. 😱
It became hugely complex trying to map redirects for old product images to new ones, so we ended up doing something else: We simply copied the asset directory with images over to the new site so they were accessible on the same URLs. What was the result of this? ⤵️
✅ The images stayed ranking and if a user clicked to visit the source, they followed the normal URL redirect and ended up on the correct page
✅ Many of the new images started to rank for similar terms - so in some instances, we had double images leading to even more traffic!
The best solution is sometimes the least complex 😊
|
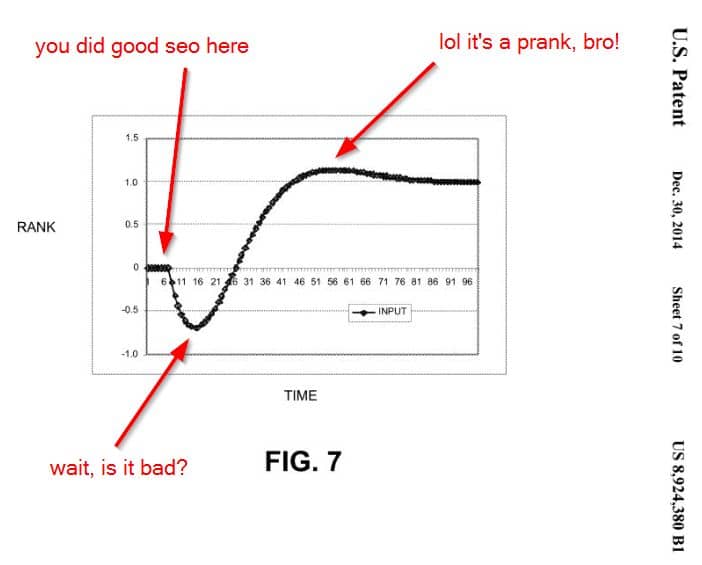
Those who cling to rankings, die.
I know it's not fashionable to look at how search engines actually work anymore, but Google has a HILARIOUS patent which is specifically designed to f* with you 🤡
♠️ If they detect a bunch of activity which makes them want to rank the page better, they could do the *reverse* and bomb the ranking. The bluff is to try and lure search engine manipulators into doing more activity.
🚦 The idea is over time, Google can correlate these sudden shifts to manipulative behaviour to determine is someone is trying to game the system.
We covered "Changing a Rank of a Document by Applying a Rank Transition Function" patent on the SEO Patent Podcast.
|
Refer subscribers and earn rewards!
|
|
|